1 系统资源监控
- Comprehensive statistics
btop: CPU, GPU, Mem, Disk (I/O), Net.htop: CPU, Mem.top: CPU, Mem.
- GPU
NVIDIA
nvitop -m full --colorful --gpu-util-thresh 10 80 --mem-util-thresh 10 80nvidia-smi
- Disk I/O
iostat
- CPU temperatures
- From
lm-sensors:sensors
- Network
Total statistics:
nloadStatistics per process:
nethogs
- Disk usage
Total statistics:
df -hFor given directories/files:
du -sh
2 用户管理
# create a normal user
sudo adduser yangrui
# set the password for an user
sudo passwd yangrui
# modify your own password
passwd
# add an user to the sudo group (administrator) without removing it from other groups
sudo usermod -aG sudo yangrui
# delete an user and its home directory
sudo deluser --remove-home yangrui
# view an user's info
id yangrui
# login as a given user
su - yangrui3 内核相关命令
# 查看当前正在使用的内核版本
uname -r
# 查看所有已安装的内核版本
dpkg --list | grep linux
dpkg --get-selections | grep linux
# 固定内核版本
sudo apt-mark hold linux-image-$(uname -r)
sudo apt-mark hold linux-headers-$(uname -r)
sudo apt-mark hold linux-modules-$(uname -r)
sudo apt-mark hold linux-modules-extra-$(uname -r)
sudo apt-mark hold linux-generic
sudo apt-mark hold linux-image-generic
sudo apt-mark hold linux-headers-generic
sudo apt-mark hold linux-libc-dev:amd64
# 恢复内核更新
sudo apt-mark unhold linux-image-$(uname -r)
sudo apt-mark unhold linux-headers-$(uname -r)
sudo apt-mark unhold linux-modules-$(uname -r)
sudo apt-mark unhold linux-modules-extra-$(uname -r)
sudo apt-mark unhold linux-generic
sudo apt-mark unhold linux-image-generic
sudo apt-mark unhold linux-headers-generic
sudo apt-mark unhold linux-libc-dev:amd644 文件权限与归属
4.1 基本文件权限
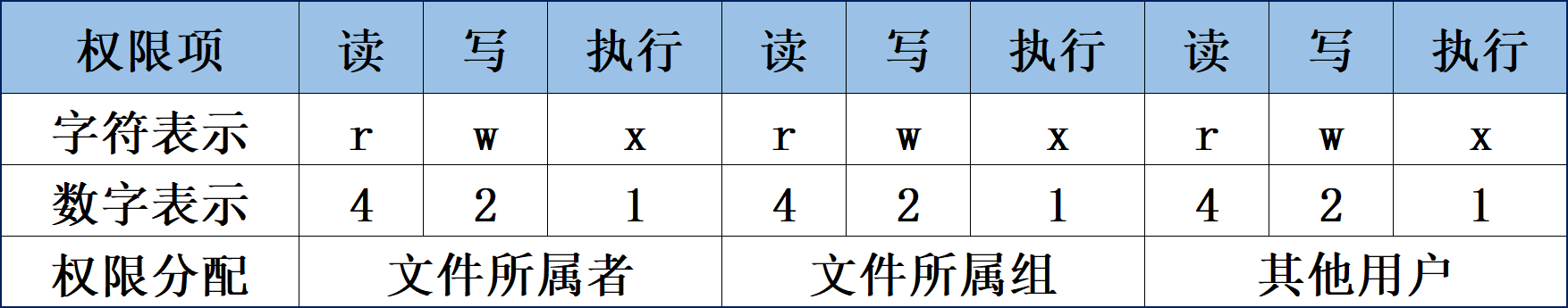
- 基本文件权限的字符及其数字表示
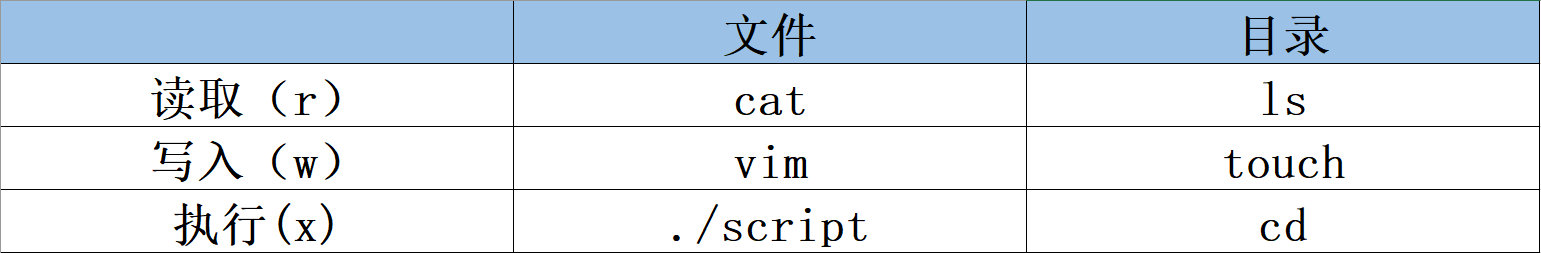
r、w和x权限对于文件和目录的区别
4.2 特殊文件权限
- SUID
SUID 是一种对二进制程序进行设置的权限,能够让二进制程序的执行者临时拥有所有者的权限,执行者应首先拥有二进制程序的执行权限。如果一个文件被赋予了 SUID 权限且其所有者拥有执行权限,则其所有者的 x 权限位变为 s,否则变为 S。
设置/取消 SUID 权限:u+s/u-s。
- SGID
对二进制程序进行设置时,能够让执行者临时拥有文件所属组的权限,执行者同样应首先拥有二进制程序的执行权限。
对目录进行设置时,则是让该目录内新创建的文件自动继承该目录的所属组。
如果一个文件或目录被赋予了 SGID 权限且其所属组拥有执行权限,则其所属组的 x 权限位变为 s,否则变为 S。
设置/取消 SGID 权限:g+s/g-s。
- SBIT
当某个目录被设置了 SBIT 权限后,该目录下的文件只可被其所有者删除。
如果一个目录被赋予了 SBIT 权限且其他用户拥有执行权限,则其他用户的 x 权限位变为 t,否则变为 T。
设置/取消 SBIT 权限:o+t/o-t。
对于数字表示法:SUID/SGID/SBIT 分别对应 4/2/1。
完整的数字表示法是:特殊权限 + 一般权限。例如:7777 是最大权限,其第一位代表特殊权限位。
4.3 修改文件权限
# 对目录进行递归操作加 -R
# 数字表示法
chmod 755 test
# 字符表示法
chmod o+x test4.4 修改文件所属
# 对目录进行递归操作加 -R
# 设置文件的所有者和所属组
chown owner:group test5 文件的隐藏属性
可以使用 chattr 和 lsattr 来设置或查看文件的隐藏属性。
6 文件访问控制列表(ACL)
利用 ACL 可以针对特定的用户或用户组设置文件的权限。
可以利用 setfacl 和 getfacl 来设置或查看文件的 ACL 权限。
如果一个文件设置了 ACL 权限,则其权限位最后一个 . 就会变成 +。
setfacl -mR u:yangrui:rwx /root
getfacl /root